This database was created for the use of managers and coaches of a Town Youth Soccer Club. The use cases include creating an account for the user (managers, coaches, parents of players), entering and storing information on the players and other participants (see Person entity), as well as entering attendence and grading each player's skill set for each practice.
Documentation includes all business rules necessary for modeling entity relationships. A few more entities may be easily incorporated into the structure, such as travel games that would record the games played by the players of the current town club with other towns. Such relationship would have a M to N associative relationship with the player and therefore would require a bridging entity.
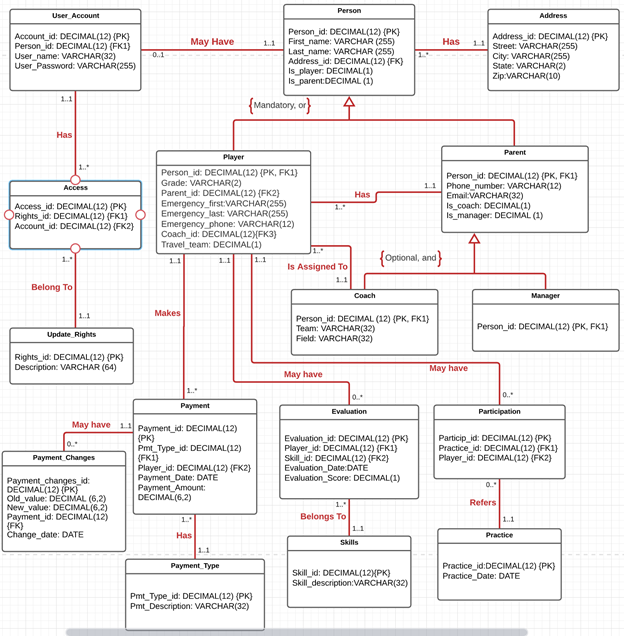
Database contains 16 entities, 5 of which are in generalization/specialization relationship and the rest are in associative relationships. The design contains bridging entities where necessary to model M:N relationships. The database also has a history table that tracks changes in fees for annual participation and uniforms.
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) above captures the structure of the database. The diagram uses traditional UML style for outlining the relationships. Specialization/generalization hierarchy is represented by Person supertype and two layers of subtypes. A Person can be either a Parent or a Player, but not both, hence the relationship is {mandatory, or}. Next level down, a Parent is a supertype for both Coach and Manager (since both positions are filled by parent-volunteers). A parent does not have to fill any of the positions for his child to play in the club. Therefore the relationship is {optional, and}.
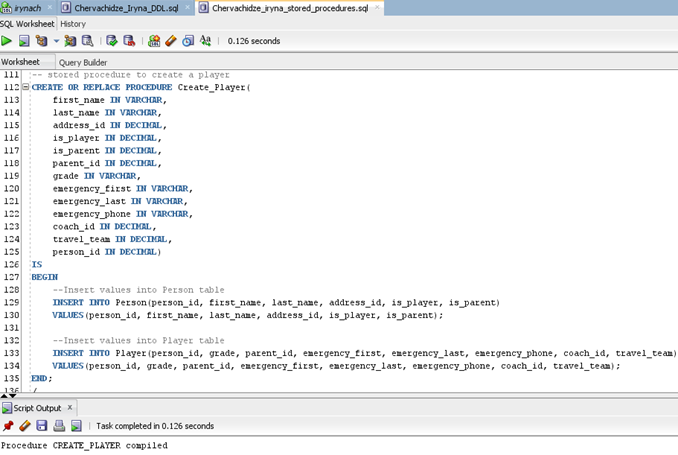
SQL implementation includes stored procedures to populate tables as well as a trigger that records changes of fees in the history table once the fee amount changes. The project includes an Oracle SQL script that contains DDL to create and populate tables and three sample queries that feature aggregate functions, joins, and subqueries. A sample stored procedure is given here. It populates the table Player. Since Player is a subtype of the Person entity, the procedure needs to update both tables with the data. I also created stored procedures for populating Person, Coach, and Payment tables. SQL script contains all these and additional procedures.
